Familiarity with basic dermal anatomy aids in understanding how to best treat conditions involving this important organ. The skin is divided into 3 distinct layers: the hypodermis (subcutis), the dermis and the epidermis.
The hypodermis is the insulation layer and is composed mostly of fat, vasculature and glands. The dermis comprises hair follicles and sebaceous glands. lt is an integral part of the connective tissue system and provides tensile strength and elasticity for the skin. Cell growth, proliferation, adhesion, migration and wound healing all begin in the dermis.
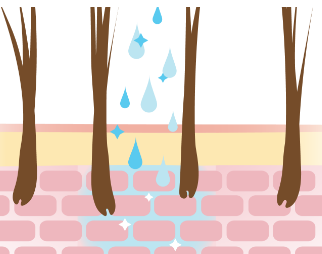
Figure. The normal epidermal barrier of a dog. The diagram shows the corneocytes and lipids working together to form a “brick-and-mortar” barrier.
These protocols have been suggested based on provided literature and are not intended to be “one size fits all.” They should be adjusted according to the individual needs of each patient.