By itself, tris-EDTA (tris-ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid) is bacteriostatic, but when used in combination with an antibiotic, it becomes bacteriocidal, decreasing the minimum inhibitory concentration of even multidrug-resistant antibiotics. It works by damaging the outer wall of bacteria, making the organisms more permeable, and has a synergistic effect with antibiotics and other agents like chlorhexidine.3,6 Tris-EDTA is also an antibiofilm agent and may help overcome resistance induced by upregulation of Pseudomonas spp. efflux pumps.3,5
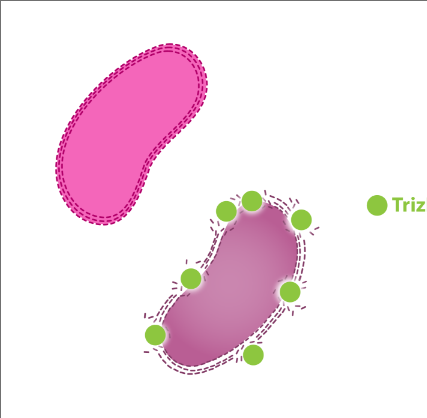
Figure. Graphic illustration of Dechra TrizEDTA technology. Tris-EDTA helps to perforate the cell wall. This action on the pathogen potentiates antimicrobial killing power.3,6
